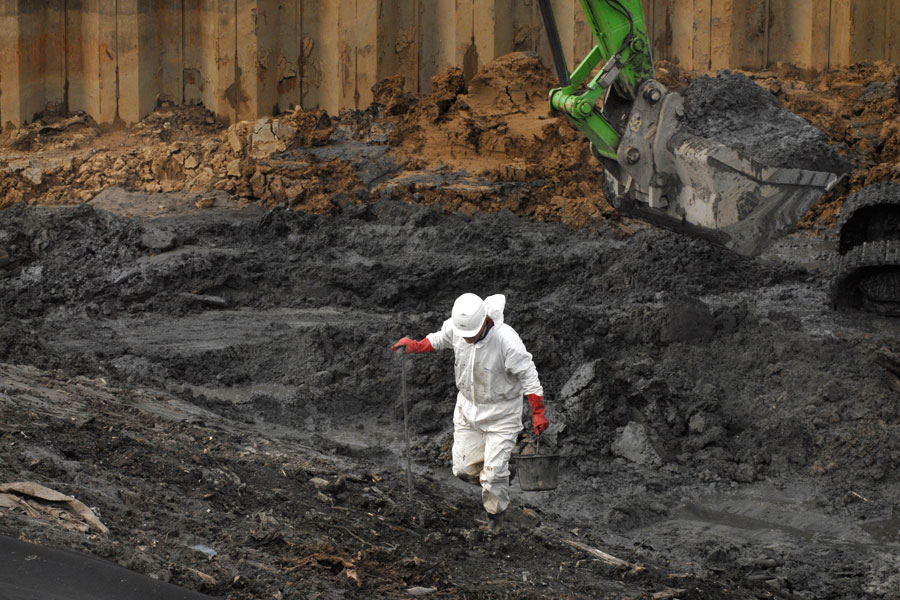
MALIBU, CA – Contaminated land presents significant challenges for construction firms, developers and environmental consultants. Whether the issue is industrial waste, petroleum hydrocarbons, heavy metals or chemicals from historic operations, contamination can delay development and pose environmental risks. Soil remediation services provided by organisations such as Mayfield Environmental Solutions use structured, science-based methods to restore impacted sites so they can be used safely and responsibly.
Modern remediation work involves a combination of investigation, soil treatment processes, site excavation strategies and innovative remediation technology. These methods are selected based on the contamination type, extent and regulatory requirements. The objective is not only to remove or neutralise harmful substances but also to support long-term environmental recovery.
This detailed guide explains the full remediation process, the technologies involved and how professionals at Mayfield Environmental Solutions determine the most suitable cleanup methods for each project.
Understanding Soil Contamination
Soil contamination occurs when hazardous substances accumulate in the ground through industrial activities, spills or improper waste handling, creating risks for human health, construction projects and surrounding environmental systems.
Common Sources of Contaminated Soil
Contaminated soil can originate from numerous industrial, commercial and residential activities. Some common sources include:
- Historical fuel storage and leaks
- Former manufacturing operations
- Agricultural chemicals
- Waste disposal sites
- Heavy-vehicle maintenance areas
- Accidental spills at construction or industrial facilities
These activities introduce pollutants such as petroleum hydrocarbons, solvents, heavy metals, pesticides, asbestos fibres and other hazardous materials. Without intervention, these contaminants can migrate into groundwater or spread across the site through surface runoff.
Key Soil Remediation Methods Used on Contaminated Sites
Different remediation methods address specific pollutants and soil conditions, combining physical removal, targeted chemical treatment or biological processes to reduce contamination levels and support safe redevelopment while meeting environmental standards and project requirements.
Soil remediation services utilise different techniques based on the severity of contamination, soil structure and regulatory requirements, and in some cases may be coordinated alongside related assessments such as mold testing remediation when indoor or structural concerns are linked to wider site impacts.
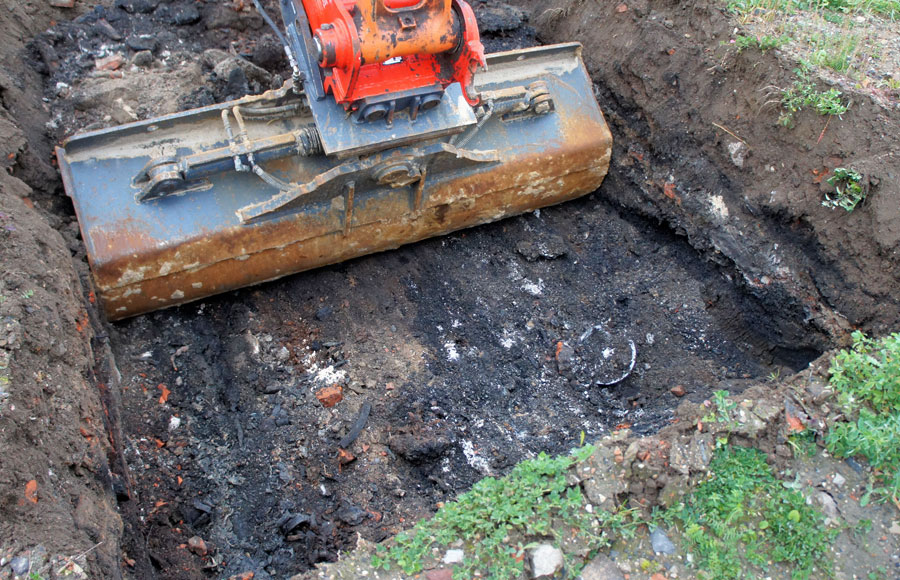
Site Excavation and Off-Site Disposal
Site excavation is one of the most common methods for removing highly contaminated soil. Heavy machinery is used to dig out affected areas, transport the soil to licensed disposal facilities and backfill the site with clean material.
Excavation is effective when:
- Contamination is shallow
- Pollutants are concentrated in a specific zone
- Construction timelines require quick cleanup
Although excavation provides immediate results, it is generally used when other soil treatment methods are unsuitable.
In-Situ Soil Treatment
In-situ treatment refers to technologies applied directly to the soil without removing it from the ground.
Common techniques include:
In-Situ Chemical Oxidation (ISCO)
Oxidants are injected into the soil to break down organic contaminants.
Bioremediation
Microorganisms are stimulated or introduced to break down hydrocarbons and other degradable pollutants.
Choosing the Right Cleanup Method: A Comparison
Below is a simplified comparison table summarising major soil remediation options and their typical applications.
| Remediation Method | Best For | Advantages | Considerations |
| Site Excavation | Localised, high-level contamination | Fast results, effective removal | Higher transport and disposal costs |
| Bioremediation | Organic pollutants like hydrocarbons | Environmentally friendly, cost-efficient | Slower process, dependent on soil conditions |
| Chemical Oxidation | Solvents and industrial chemicals | Rapid breakdown of contaminants | Requires controlled handling |
| Soil Vapour Extraction | Volatile contaminants | Minimal soil disturbance | Not effective for non-volatile pollutants |
| Soil Washing | Metals and dense contaminants | Recovers reusable soil fractions | Requires specialised equipment |
| Thermal Desorption | High-toxicity pollutants | Suitable for complex contamination | High energy consumption |
Selecting the right method depends on contamination type, site size, development plans and regulatory standards. Environmental consultants use risk-based assessments to recommend the most effective approach.
Modern Remediation Technology and Innovation
Advancements in remediation technology continue to improve treatment efficiency and environmental outcomes. Some recent innovations include:
Real-Time Monitoring Systems
Sensors and digital tools allow professionals to track contaminant breakdown rates, groundwater conditions and vapour movements in real time.
High-Temperature Thermal Systems
These systems rapidly treat soil containing complex chemical contaminants while ensuring controlled emissions and safety.
Enhanced Bioremediation
Engineered microbial blends and improved nutrient delivery systems increase degradation rates for petroleum hydrocarbons.
Sustainable Remediation Practices
Techniques that minimise energy use, reduce waste and promote environmental recovery are increasingly important. Examples include low-energy bioremediation and the reuse of treated soil on-site to reduce transportation impact.
Environmental Recovery and Site Redevelopment Benefits
The ultimate purpose of soil remediation services is not only to remove contaminated soil but also to support long-term environmental health.
Improved Soil Quality
Treatment restores the natural structure and fertility of soil, enabling landscaping, vegetation growth or ecological restoration.
Safer Construction and Development
Clean and compliant soil provides a safe foundation for residential, commercial and industrial projects.
Challenges in Soil Remediation Projects
Soil remediation projects often encounter complex contamination patterns, variable subsurface conditions and strict regulatory expectations, requiring careful planning, precise execution and ongoing technical evaluation to achieve reliable, compliant and long-term site restoration outcomes.
Despite technological progress, remediation projects can face several challenges:
Complex Pollutant Mixtures
Sites may contain a combination of organic and inorganic contaminants that require multiple treatment methods.
Project Timelines
- Construction schedules sometimes demand accelerated cleanup, influencing method selection.
- Environmental professionals evaluate all these factors during planning to ensure successful outcomes.
Contact Mayfield Environmental Solutions
Restoring contaminated land requires careful assessment, thoughtful planning and the use of appropriate soil remediation services. By combining investigation, soil treatment, site excavation and modern remediation technology, environmental professionals ensure that impacted sites are managed responsibly and prepared for safe redevelopment.
Effective cleanup methods not only remove hazardous substances but also support long-term environmental recovery, protect groundwater resources and reduce future risks. As construction demands grow and regulatory expectations increase, understanding the full remediation process becomes essential for developers, consultants and project teams working toward sustainable land use.
For more information or to discuss your project requirements, you can contact us for guidance on suitable remediation approaches.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are soil remediation services?
Soil remediation services involve assessing, managing and treating contaminated soil to meet environmental standards. These services use various cleanup methods, such as site excavation, chemical treatment and bioremediation.
How do experts determine the right treatment method?
Consultants conduct sampling, laboratory tests and risk assessments to understand the type, concentration and location of contaminants. This data guides the selection of appropriate cleanup methods.
Is site excavation always necessary?
Excavation is used when contamination is highly concentrated or when fast removal is required. Many projects can be handled with in-situ or ex-situ soil treatment technologies.
How long does soil remediation take?
Timelines vary based on contamination levels, selected treatment methods and regulatory requirements. Some methods deliver quick results, while biological processes may take several months.
Can treated soil be reused?
Yes, depending on the method and final contamination levels. Soil washing, thermal desorption and some bioremediation processes allow soil to be reused safely on-site.