MALIBU, CA – Removing an underground storage tank (UST) is a highly regulated and complex process that involves careful planning, coordination, and execution. The process goes far beyond simply excavating a tank. It encompasses initial assessment, permitting, tank decommissioning, excavation, soil testing, possible remediation, and final reporting. Understanding the steps and potential challenges is essential for property managers, fuel station owners, and facility operators.
This guide by Mayfield Environmental Solutions explains the underground storage tank removal process, including tank excavation, oil tank removal, fuel tank removal services, environmental considerations, and regulatory compliance. It also provides a clear educational timeline and compliance framework to help stakeholders prepare for a smooth and safe removal project.
Key Phases in the Tank Removal Process
Underground storage tank removal involves several coordinated phases. Each phase has specific requirements that ensure safety, compliance, and environmental protection. The table below summarizes the major steps:
| Phase | Description |
| Planning & Permitting | This phase involves evaluating site conditions, identifying applicable regulations, and obtaining necessary permits from local and federal agencies. |
| Pre-Excavation Preparations | Includes marking utilities, disconnecting tank piping, removing ancillary equipment, and cleaning the tank interior. Proper preparation reduces the risk of hazards during excavation. |
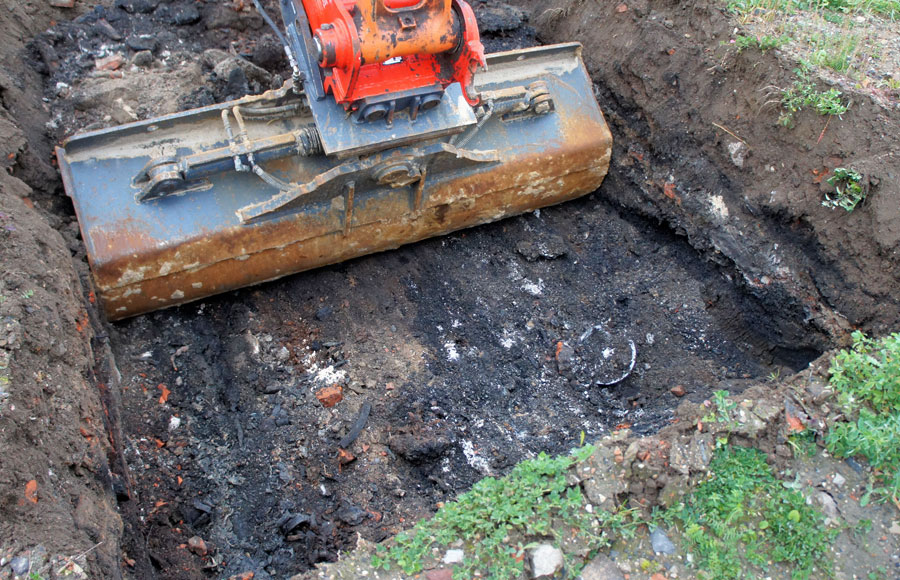
| Tank Excavation & Removal | Excavators carefully dig around the tank to remove it safely. Tanks are lifted or rolled out, and any residual product is contained and disposed of according to regulations. |
| Soil Sampling & Analysis | Soil around and below the tank is sampled to detect potential contamination. Analysis ensures that corrective actions, if needed, are guided by accurate data. |
| Corrective Action / Remediation | If contamination is found, soil or groundwater may need to be treated, removed, or remediated. Remediation ensures the site meets regulatory standards. |
| Backfilling & Site Restoration | After removal and remediation, the excavation site is backfilled with clean soil, compacted, and restored to its original condition. |
| Final Reporting & Regulatory Closure | Documentation is prepared and submitted to regulatory agencies. Closure is verified and approved based on compliance with all requirements. |
Each step requires careful planning and coordination with underground storage tank removal contractors or environmental contracting services to ensure compliance and safety.
Factors That Influence the Duration of Tank Removal
The timeline of an underground storage tank removal project can vary based on several factors. Understanding these influences is essential for planning, risk management, and budgeting.
Regulatory Permitting and Notifications
A critical factor in tank removal is regulatory compliance. Owners must submit permits or notifications to environmental agencies before starting any work. Agencies may require detailed information about the tank, such as size, contents, material, and site history. Regulatory review processes vary by jurisdiction, which can impact the overall project timeline.
Site Accessibility and Complexity
The location of the tank plays a major role in determining the complexity of excavation. Tanks near building foundations, utilities, or underground structures require additional planning. Challenging access may involve specialized excavation techniques, protective measures, and the use of specific equipment to prevent damage.
Contamination and Soil Conditions
The presence of contamination affects the project significantly. Soil or groundwater contamination may require a comprehensive corrective action plan, including excavation, treatment, or bioremediation. Site conditions such as soil type, rock layers, and groundwater levels also influence excavation methods and the choice of equipment.
Contractor Resources and Scheduling
The availability of experienced contractors for underground storage tank removal or fuel tank removal services can affect the project schedule. Projects require skilled operators, specialized equipment, and coordination among multiple teams. Contractor availability and resource allocation can create scheduling considerations.
Agency Review and Reporting
After the physical removal and soil sampling, regulatory agencies review reports, lab results, and closure documentation. Agencies may request additional testing or clarification, which impacts the duration of project completion. Proper preparation and documentation help minimize delays during this phase.
Step-by-Step Guide to Underground Tank Removal
Understanding the sequence of tasks in underground tank removal is essential for stakeholders to effectively manage expectations, allocate resources, and ensure compliance with safety and environmental regulations. A clear step-by-step plan helps minimize risks, avoid delays, and maintain project efficiency throughout the removal process.
Initial Assessment and Site History Review
The first step is a thorough review of the site and tank history. This includes reviewing records of prior leaks, tank age, material, capacity, and maintenance history. Identifying potential risks during this phase ensures that safety and regulatory requirements are addressed early.
Permitting and Regulatory Notification
Obtaining the necessary permits and notifying regulatory authorities is a mandatory step. Authorities may require details about the tank removal plan, including methods, safety measures, and potential environmental impacts. Compliance with these requirements is critical to avoid penalties and ensure a smooth process.
Pre-Excavation Preparations
Before excavation, the site must be properly prepared. Utilities should be located and marked to avoid accidental damage. Piping and ancillary equipment are disconnected and removed. The tank interior is cleaned to eliminate residual fuel or oil, reducing the risk of fires, explosions, or environmental contamination.
Tank Excavation and Removal
Excavation requires careful planning and execution. Excavators dig around the tank while taking precautions to prevent collapse of the excavation walls. Tanks are lifted, rolled out, or otherwise removed depending on size and configuration. Any residual contents are safely contained and transported for proper disposal.
Soil Sampling and Analysis
After tank removal, soil samples are collected from the tank cavity and surrounding area. Analysis of these samples determines whether contamination has occurred and guides any required remediation steps.
Corrective Action and Remediation
If contamination is detected, corrective actions are implemented. This may involve soil excavation, treatment, stabilization, or in-situ remediation techniques. Ensuring that all contamination is addressed is critical for compliance with environmental regulations and for protecting human health and the environment.
Backfilling and Site Restoration
Once removal and remediation are complete, the excavation area is backfilled with clean soil, compacted, and graded. Any landscaping, paving, or structural surfaces disturbed during excavation are restored. Proper site restoration is necessary to maintain safety and functionality.
Final Reporting and Regulatory Closure
The final step involves preparing comprehensive documentation, including soil analysis reports, remediation details, and compliance records. These documents are submitted to regulatory authorities for review. Approval of these reports indicates that the tank has been removed and the site meets all applicable environmental and safety standards.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Proper adherence to federal and local regulations ensures safe underground storage tank removal, minimizes environmental risks, prevents contamination, and protects workers, property, and surrounding communities throughout the excavation and decommissioning process.
- Federal UST Regulations – Federal rules define an underground storage tank as a system that stores at least 10% of its volume underground. Tanks used for petroleum, fuel, or hazardous substances are subject to strict closure, removal, and corrective action regulations.
- Closure and Recordkeeping – Temporary closure of tanks is allowed in some circumstances, but permanent removal or decommissioning is typically required to prevent environmental hazards. Regulatory authorities require detailed records and documentation, including the condition of the tank, soil test results, and remediation actions.
- Safety Measures During Excavation – Safety is paramount during tank removal. Air monitoring, shoring, and proper handling of residual contents are essential. Excavation areas must be secured, and workers must follow strict protocols to prevent accidents, contamination, or exposure to hazardous substances.
- Environmental Liability – Leaking or abandoned tanks can create ongoing liability for property owners. Proper removal and compliance with environmental standards mitigate the risk of soil and groundwater contamination, reducing future legal and financial liabilities.
Tips for Efficient Tank Removal
- Engage regulatory authorities early to address potential issues in advance.
- Conduct thorough site assessments to identify risks and plan for remediation if needed.
- Schedule contractors and resources ahead of time to avoid delays.
- Use local laboratories for soil analysis to expedite compliance documentation.
- Maintain comprehensive records and reports to facilitate smooth regulatory review.
- Plan for unexpected conditions, such as underground utilities or challenging soil conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. How is the tank physically removed?
Tanks are excavated using specialized equipment. Care is taken to prevent collapse of the excavation area, and tanks are safely lifted or rolled out. Residual fuel or oil is contained for proper disposal.
Q. What happens if contamination is discovered?
Contamination triggers corrective actions, which may include soil excavation, treatment, or bioremediation. The site must meet regulatory standards before closure.
Q. Is it possible to leave the tank in place?
Some jurisdictions allow fill-in-place for tanks that are difficult to remove. However, complete removal is often preferred to eliminate liability and ensure compliance.
Q. Do authorities inspect the removal process?
Yes, regulatory representatives may observe or inspect tank removal, soil sampling, and remediation activities to ensure compliance.
Q. What factors influence the duration of a removal project?
Regulatory requirements, site accessibility, soil conditions, contamination, and contractor availability all impact the duration of the project.
Contact Mayfield Environmental Solutions
Underground storage tank removal, including underground tank removal, underground fuel tank removal, oil tank removal, and storage tank removal services, is a complex process that requires careful planning, execution, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Property managers and fuel site operators must work closely with qualified underground storage tank removal contractors and environmental contracting services to ensure safe removal, proper remediation, and regulatory closure. By understanding the steps involved, potential challenges, and key considerations, stakeholders can successfully manage tank removal projects while protecting people, property, and the environment.
Proper preparation, adherence to safety protocols, and thorough documentation are essential to achieving a successful outcome. Understanding the full process of tank excavation and removal and underground storage tank decommissioning ensures compliance, safety, and environmental protection for every project. For professional guidance and reliable services, contact Mayfield Environmental Solutions to discuss your underground storage tank removal needs.