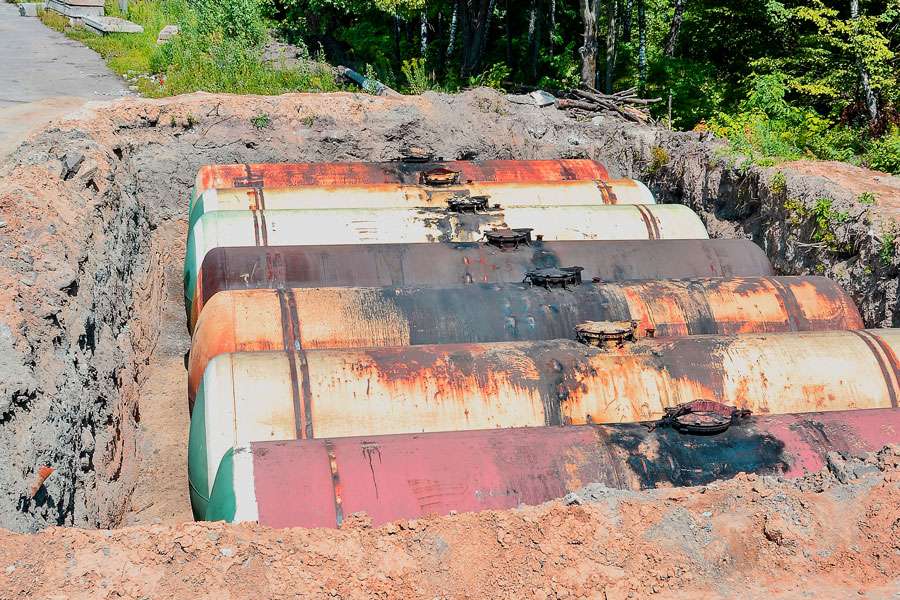
MALIBU, CA – Underground oil tanks, often installed decades ago, were once common for storing heating oil or fuel. However, over time, these tanks can deteriorate, leak, or become obsolete. Underground oil tank removal is a critical step for homeowners and businesses to ensure safety, prevent environmental contamination, and comply with regulations.
Mayfield Environmental Solutions provides expert guidance and professional services to safely remove and manage these tanks. This guide provides a detailed overview of the removal process, associated costs, environmental considerations, and best practices for both residential and commercial properties. Understanding the risks and responsibilities associated with old or abandoned tanks can help property owners make informed decisions and maintain compliance with environmental laws.
Underground Oil Tank Removal May Be Necessary
Underground storage tanks (USTs) can pose serious risks if not properly maintained or decommissioned. Potential hazards include:
- Soil and groundwater contamination from leaks
- Environmental liability for property owners
- Safety risks due to residual fuel or unstable tank structures
- Regulatory penalties for non-compliance
Removing old oil tanks is essential not only for environmental protection but also for property value, liability mitigation, and long-term safety. Early removal can prevent costly cleanups, legal issues, and even structural damage to surrounding areas caused by leaking tanks.
Types of Tanks and When Removal is Necessary
Different types of tanks require different approaches. Understanding what you have helps determine the appropriate removal method.
| Tank Type | Typical Use | Common Issues | Recommended Action |
| Residential oil tank | Heating oil storage | Rust, leaks, soil contamination | Residential oil tank removal |
| Commercial fuel tank | Gasoline, diesel, or heating oil | Corrosion, regulatory requirements | Commercial oil tank removal |
| Abandoned or old tanks | Fuel storage no longer in use | Environmental liability | Underground storage tank removal |
| Underground fuel tanks | Gas stations or industrial sites | Leaks, contamination, inspection needs | Underground fuel tank removal |
Knowing the type of tank you are dealing with helps determine the proper precautions, permits, and cleanup measures necessary for safe removal.
Step-by-Step Process for Underground Oil Tank Removal
Undertaking underground oil tank removal requires careful planning, safety precautions, and adherence to environmental regulations. Following a structured process ensures both residential and commercial properties remain safe and compliant. Here is a step-by-step overview:
1. Site Inspection and Assessment
- Identify the type, size, and condition of the tank
- Conduct soil testing to detect contamination
- Determine regulatory requirements for UST closure
- Assess potential hazards for workers and surrounding areas
2. Obtaining Permits and Notifications
- Notify local environmental authorities if required
- Obtain permits for excavation and fuel disposal
- Schedule inspections as mandated by local or state regulations
3. Tank Drainage and Cleaning
- Safely pump out remaining fuel
- Clean residual sludge to reduce hazards
- Ensure proper storage or disposal of extracted oil according to environmental standards
4. Excavation and Removal
- Carefully dig around the tank to avoid spills
- Remove the tank from the site
- Inspect surrounding soil for contamination and structural issues
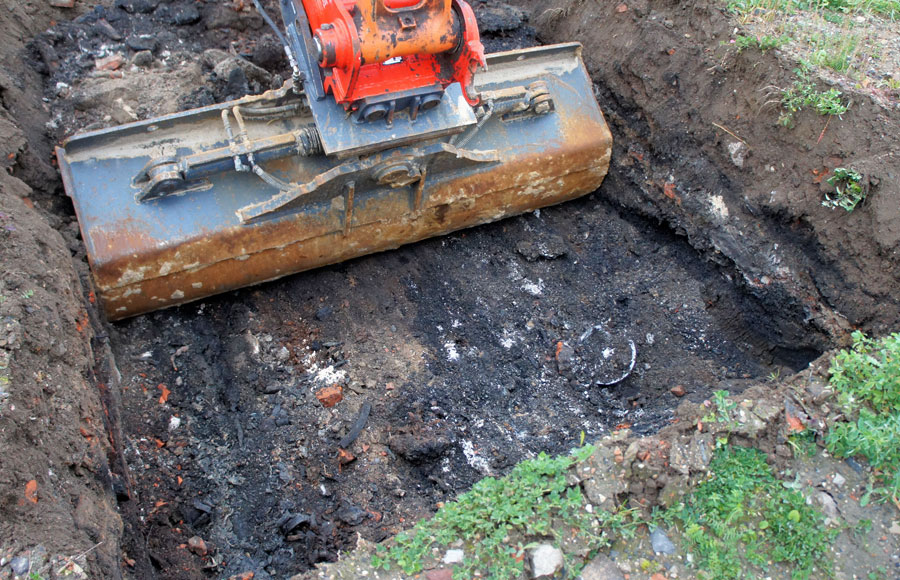
5. Contamination Cleanup (if necessary)
- Excavate contaminated soil for treatment or disposal
- Replace or treat soil to meet safety standards
- Conduct follow-up soil testing to ensure compliance
6. Site Restoration
- Backfill excavation with clean soil
- Restore landscaping, pavement, or structures
- Document the removal process for regulatory compliance and future reference
Following a structured process ensures that underground oil tank removal is conducted safely, efficiently, and in compliance with all environmental regulations.
Factors Affecting Tank Removal Cost
Tank removal cost can vary depending on several factors. Understanding these can help property owners plan and budget effectively.
- Tank size and material – Larger or older steel tanks may be more complex and labor-intensive to remove.
- Location – Accessibility of the tank impacts excavation efforts and equipment needed.
- Soil contamination – Cleanup adds to the cost if leaks or spills have occurred.
- Type of property – Residential vs. commercial projects may require different permits and procedures.
- Disposal requirements – Fuel, sludge, and contaminated soil must be disposed of according to local regulations.
| Factor | Impact on Cost |
| Tank size | Larger tanks = higher removal costs |
| Age & condition | Corroded tanks require more labor |
| Soil contamination | Cleanup increases cost significantly |
| Site accessibility | Difficult terrain or tight spaces = higher labor cost |
| Regulatory compliance | Permits and inspections add fees |
Being aware of these factors helps property owners anticipate expenses and make informed decisions when hiring oil tank removal services.
Residential vs. Commercial Oil Tank Removal
Residential oil tank removal typically involves smaller-scale excavation and limited cleanup, while commercial oil tank removal requires larger equipment, extensive soil testing, and stricter regulatory compliance due to higher fuel volumes and environmental risks.
Residential Oil Tank Removal
Residential oil tanks are commonly found in older homes for heating oil storage. Residential oil tank removal involves:
- Small-scale excavation
- Limited contamination cleanup in most cases
- Documentation for home sale, renovation, or regulatory compliance
Even though residential removals are usually smaller in scale, ensuring proper cleanup is essential to prevent potential liability or soil contamination.
Commercial Oil Tank Removal
Commercial sites, such as gas stations or industrial facilities, often have underground fuel tanks storing large volumes of fuel. Commercial oil tank removal requires:
- Detailed environmental assessment and soil testing
- Larger excavation equipment and safety measures
- Comprehensive contamination cleanup, often including specialized disposal
- Compliance with stricter regulations for commercial properties
Due to the larger scale and higher potential liability, commercial oil tank removal often involves more planning, inspection, and documentation than residential projects.
Environmental Responsibility and Risk Mitigation
Proper tank removal mitigates environmental and legal risks. Key responsibilities include:
- Preventing soil and groundwater contamination through proper extraction and cleanup
- Disposing of fuel and sludge responsibly according to regulations
- Documenting UST closure for future property transactions
- Conducting contamination cleanup and site restoration when required
By taking these steps, property owners minimize liability and promote long-term sustainability. Regulatory compliance not only protects the environment but also ensures the property can be safely sold or developed in the future.
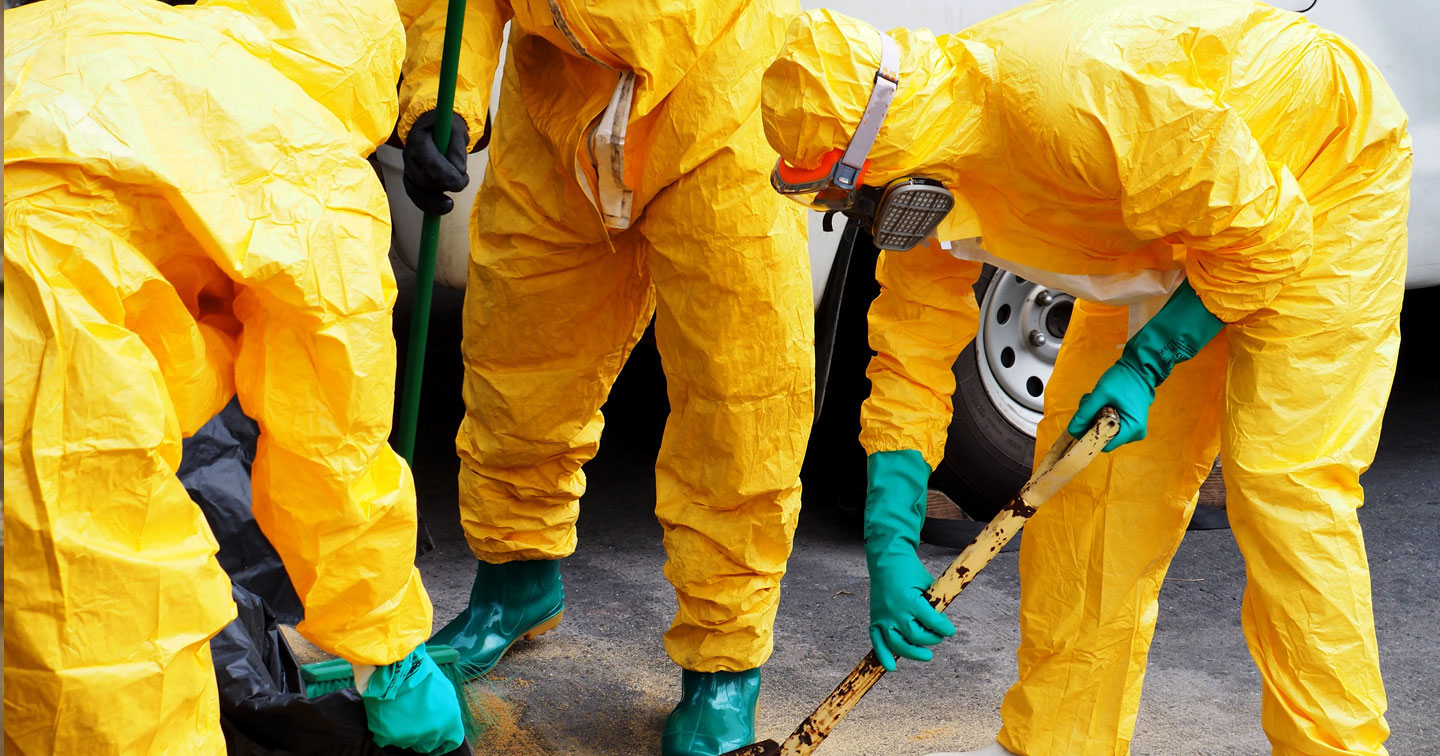
Safety Considerations During Removal
Safety is critical when handling underground oil tanks. Potential hazards include explosive vapors, residual fuel, heavy equipment accidents, and exposure to contaminated soil. Precautions should include:
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and respirators
- Adherence to proper excavation procedures to prevent cave-ins
- Monitoring air quality to detect fuel vapors
- Professional handling and disposal of all extracted materials
Engaging certified oil tank removal services ensures that safety standards are strictly followed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How long does underground oil tank removal take?
Removal typically takes 1–3 days for residential tanks. Commercial tanks may require a week or more depending on size, contamination, and permitting requirements.
Q2: Can I remove the tank myself?
DIY removal is strongly discouraged. Professional oil tank removal services have the necessary equipment, training, and permits to safely remove tanks without risking environmental damage or personal injury.
Q3: How much does it cost to remove an underground oil tank?
Costs vary depending on tank size, location, and soil contamination. Residential tank removal can range from $1,500 to $5,000, while commercial removal may exceed $10,000, particularly if soil remediation is required.
Q4: Is soil testing necessary?
Yes. Soil testing identifies contamination and helps determine if cleanup is required, protecting both health and legal interests.
Q5: What happens after tank removal?
The site is backfilled and restored. Contaminated soil is treated or replaced, and documentation is provided for regulatory compliance and future property transactions.
Contact Mayfield Environmental Solutions
Proper underground oil tank removal is an essential step for homeowners and business property owners alike. Whether dealing with residential oil tank removal or commercial oil tank removal, the process safeguards property, protects the environment, and reduces liability.
By understanding the types of tanks, removal steps, costs, and environmental responsibilities, property owners can make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and ensure compliance with all applicable regulations. Engaging professional oil tank removal services guarantees safety, proper disposal, and comprehensive site restoration. Taking these steps not only addresses immediate hazards but also secures long-term property value and environmental stewardship.
Investing in proper tank removal today can prevent costly cleanup, legal issues, and environmental damage in the future, making it a responsible choice for any property owner. For expert assistance with underground oil tank removal, contact Mayfield Environmental Solutions today to schedule a consultation and ensure safe, compliant, and efficient tank removal.